Compliance and Digitalization – From Automation to AI
#rethinkcompliance Blog | Post from 15.06.2024
Enhancing the resilience of the risk and compliance program has become a growing requirement among auditors and regulators, as reflected in numerous legislative frameworks. The challenge resides in successfully transitioning to a digital format while achieving efficiency amidst ever growing volatility. The implementation of automation, alongside artificial intelligence and effectively coordinated policies and procedures, contributes significantly to the optimization of this process.
Situation of the Head of Compliance
Overseeing internal compliance regulations presents significant challenges, irrespective of whether the organization operates on a national, international, or global scale. It is essential to coordinate the various entities within the intricate organizational network while also considering the regionally distinct, overlapping, and frequently conflicting regulatory requirements. Here, the compliance risks associated with the particular business model are also significant.
The responsibility for this task is managed by the Head of Compliance or the compliance departments through the issuance of policies and procedures (P&P). These internal regulations facilitate the consistent application of processes related to embargo and sanctions monitoring across the entire group, for example. This is accomplished through the creation of written documents that uniformly outline the guidelines and regulations for the group. The objective is to guarantee successful and thorough execution within the relevant subsidiaries by utilizing checkpoints referred to as controls.
The basis: Policies & Procedures
There are two primary motivations for developing new policies and procedures or modifying existing ones:
- First, the necessity to comply with mandates from external organizations that the organization is required to adhere to. Alongside the topics mandated by regulatory authorities or legislative bodies, these also encompass voluntary commitments made by interest groups, guidelines for implementation, consultation documents, or actions requested by the public or society at large.
- Concurrently, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of each institution, which are contingent upon the respective organization. In pursuit of this objective, each institution conducts a risk assessment a minimum of once annually, which, informed by the business model, focuses on the particular compliance risks. The subsequent mitigation measures, along with their efficiency criteria, are then converted into organizational directives that should ideally be detailed to the level of controls.
Alongside the multitude of requirements and their growing volatility, the primary challenges facing compliance management are effectiveness and efficiency. On the one hand, it is essential to maintain communication with the regulatory bodies and to effectively oversee the implementation process, especially as the timelines for implementation continue to shorten.
On the other hand, it is essential to avoid the establishment of redundancies and to enhance organizational efficiency through the provision of necessary transparency. One advantageous outcome of this is the swift handling of requests from the audit department, external auditors, or the regulatory authority.
Practical Application
Nevertheless, merely developing and directing the implementation of policies and procedures is insufficient. It is essential to adapt the diverse operational processes and systems of all impacted entities and branches. Generally, it can be inferred that this adaptation cannot be managed centrally through Group Compliance; rather, it must be executed in a decentralized manner. Moreover, it is essential to consider the additional requirements of these decentralized units along with their particular legal circumstances. In the worst case, the requirements of the group may conflict with the legal requirements. A clear illustration of this is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which imposes stringent data protection standards within Europe and stands in opposition to transparency laws in various other nations and their respective legal frameworks.
The systematic execution of these policies and procedures thus presents a complex challenge that should not be overlooked, and it can be effectively facilitated through the provision of suitable IT support.
Requirements to IT
To facilitate the structured processing and execution of policies and procedures for the compliance department, it is essential to establish a workflow that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the group. This ensures that the tasks and their associated responsibilities are clearly defined and easily observable. The current implementation status of the policies and procedures may be inquired about at any time, particularly in relation to external audits.
An additional significant feature is the transformation of the P&Ps from unstructured text into a structured format that is appropriate for subsequent tasks. This can be accomplished through a control matrix (see Figure 1), which compares the test objects along the y-axis with the controls along the x-axis, thereby facilitating a clear description of the P&Ps. The matrix is then filled according to the contents of the P&P's.
In conjunction with comprehensive reporting and an extensive logging functionality that documents each step of the workflow, you can readily supply information to regulators and auditors whenever necessary. This guarantees the integrity of the group and the uniformity of the risk and compliance program, reduces the required effort and related costs, and results in a proficient and effective compliance organization.
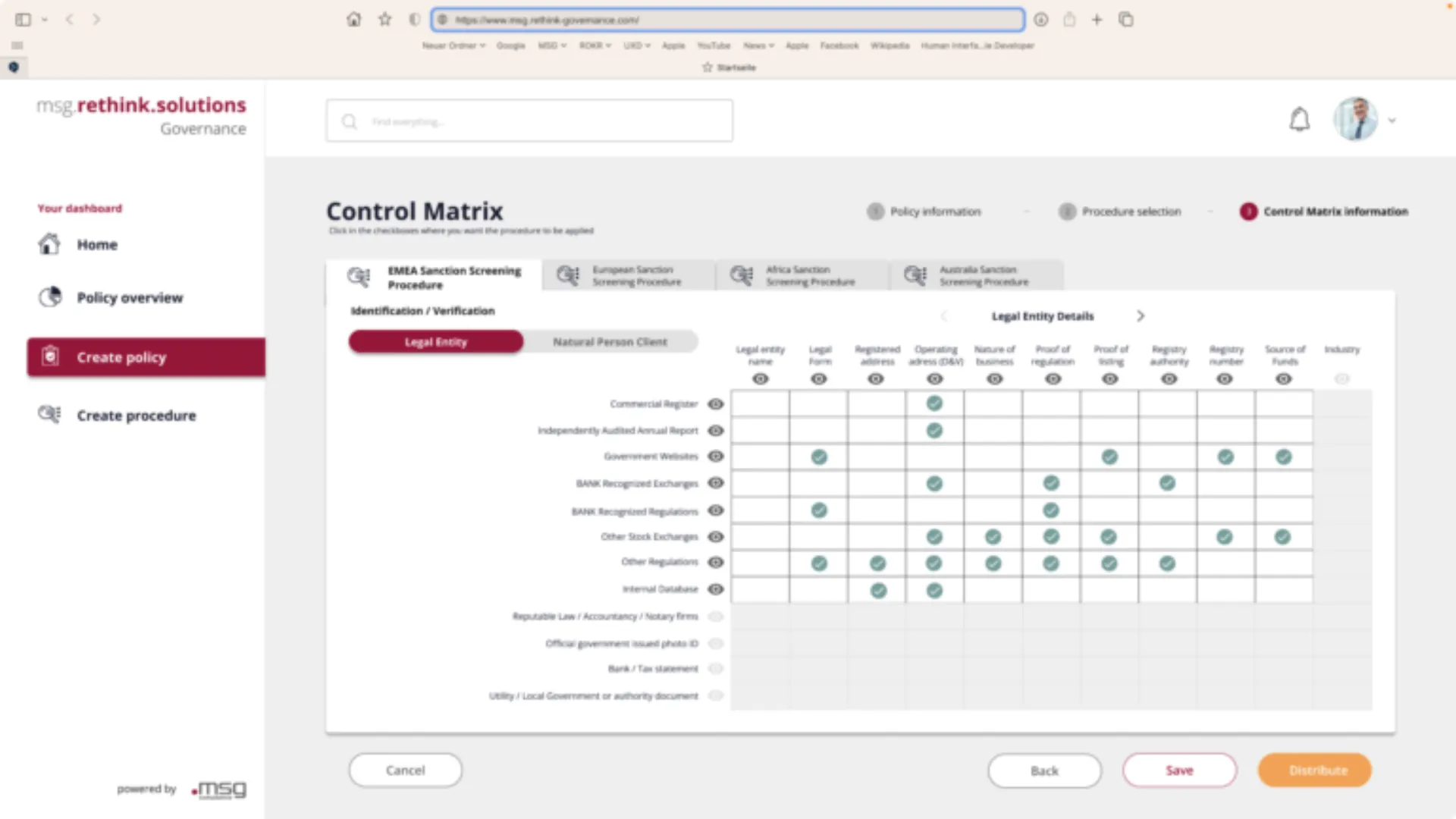
Figure 1 – Representation of a control matrix that connects the test projects with the requisite controls, thereby facilitating a clear depiction of the requirements that need to be implemented.
The Use of AI
Generally, organizations tend to possess a substantial array of established policies and procedures. The process of converting all these documents into an IT solution would entail an immense workload that cannot be accomplished through manual efforts. This is where AI comes into play. Utilizing appropriately trained large language models, all current P&Ps are analyzed and transferred to the target structure. In a downstream quality assurance procedure, the results may be evaluated for both completeness and accuracy. This allows for the rapid initial setup of the system. The process of legal change can largely be automated through digital means.
Additionally, users have access to various functionalities for the analysis of unstructured data. The summary function allows users to swiftly gain an understanding of the content of newly introduced legal texts, whereas the diff function facilitates the identification of modifications, enabling them to adjust their P&Ps as necessary, particularly in response to changes in regulatory requirements. The platform offers a tool that enables the fast and dependable adaptation or creation of internal guidelines, which can subsequently be implemented in a clear and understandable way.
Outlook
Structuring the P&Ps is only the first step. To achieve complete automation of the compliance process, it is essential to establish or integrate it within a centralized data and application platform.
This enables the alignment of rules and settings within the operational systems, such as anti-money laundering, sanctions monitoring, and fraud detection. This results in uniformity among the monitoring systems, several of which are utilized in distinct ways across the different entities.
An additional consideration is the aggregation of pertinent information across the group for compliance purposes, which is presented in a concise format for the management board, thereby allowing for a comprehensive overview of all critical events and risks.
The implementation of this automation process significantly simplifies the responsibilities of the compliance department, encompassing roles such as compliance officers, money laundering officers, policy advisors, and business analysts. It allows for the management of the organization from this standpoint, relying on data and processes that are assured in quality.
Author

Dirk Findeisen
Managing Partner
Expert for Financial Crime Compliance | 20+ Years of Experience in Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC), Data Management, Advanced Analytics, and Corporate Performance Management | Author, Speaker, Lecturer